OWASP Threat Dragon
Setting up the web application environment variables for Threat Dragon.
Configuring Environment Variables
Environment variables can be configured by exporting variables to your terminal from which you’ll be running Threat Dragon, or by using a .env local file.
Values for the environment variables
-
In your github account, go to
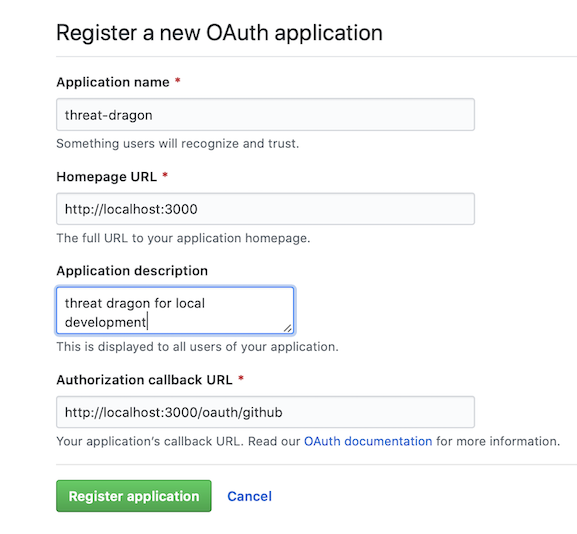
Settings -> 'Developer settings' -> 'OAuth Apps' -> 'New OAuth App' - fill out the form with the following:
- Application name: not critical, suggest something like ‘Threat Dragon’
- Homepage URL:
http://localhost:3000 - Application description: not critical, for example ‘Threat Dragon local development’
- Authorization callback URL:
http://localhost:3000/oauth/github
-
Register the application, an example screenshot is shown below.
-
In this new OAuth App, note the values for the 20 character long Client ID (used here
01234567890123456789) and the 40 character long Client Secret (used here0123456789abcdef0123456789abcdef01234567) - Generate a random 32 character hexadecimal key (something like
11223344556677889900aabbccddeeff)
You now have all the info to set up the environment variables.
Using Dotenv
If you are using dotenv then place a file named .env at the root of the project with your environment variables. An example.env is provided as a reference. Threat Dragon will then load any variables in this file as environment variables, and you do not need to setup the environment variables from the command line.
Using Command line
If you are not using dotenv, then the environment variables can be set from the command line.
MacOS / Linux
For MacOS and Linux go into the terminal from which you start Threat Dragon and enter at the command line:
- GITHUB_CLIENT_ID from Client ID above, for example
export GITHUB_CLIENT_ID=01234567890123456789 - GITHUB_CLIENT_SECRET from Client Secret above, for example
export GITHUB_CLIENT_SECRET=0123456789abcdef0123456789abcdef01234567 export NODE_ENV=developmentexport SESSION_STORE=local- SESSION_SIGNING_KEY as the random 32 character hexadecimal key, for example
export SESSION_SIGNING_KEY=11223344556677889900aabbccddeeff - SESSION_ENCRYPTION_KEYS has the same 32 character key, for example
export SESSION_ENCRYPTION_KEYS='[{"isPrimary": true, "id": 0, "value": "11223344556677889900aabbccddeeff"}]' - GITHUB_SCOPE - set this to
repoif you want access also to private repos
Note that we are using the example values for these variables, and the values obtained in the ‘Values for the environment variables’ section must be used instead.
Windows
Similarly for Windows, from the terminal used to start Threat Dragon enter at the command line:
set GITHUB_CLIENT_ID=01234567890123456789set GITHUB_CLIENT_SECRET=0123456789abcdef0123456789abcdef01234567set NODE_ENV=developmentset SESSION_STORE=localset SESSION_SIGNING_KEY=11223344556677889900aabbccddeeffset SESSION_ENCRYPTION_KEYS='[{"isPrimary": true, "id": 0, "value": "11223344556677889900aabbccddeeff"}]'
Note that we are using the example values for these variables, and the values obtained in the ‘Values for the environment variables’ section must be used instead.
Check it is running
You should now be able to start Threat Dragon web application using npm start and then navigate in a browser to “http://localhost:3000/”
Example OAuth registration
Example screenshot of registering a new OAuth application: